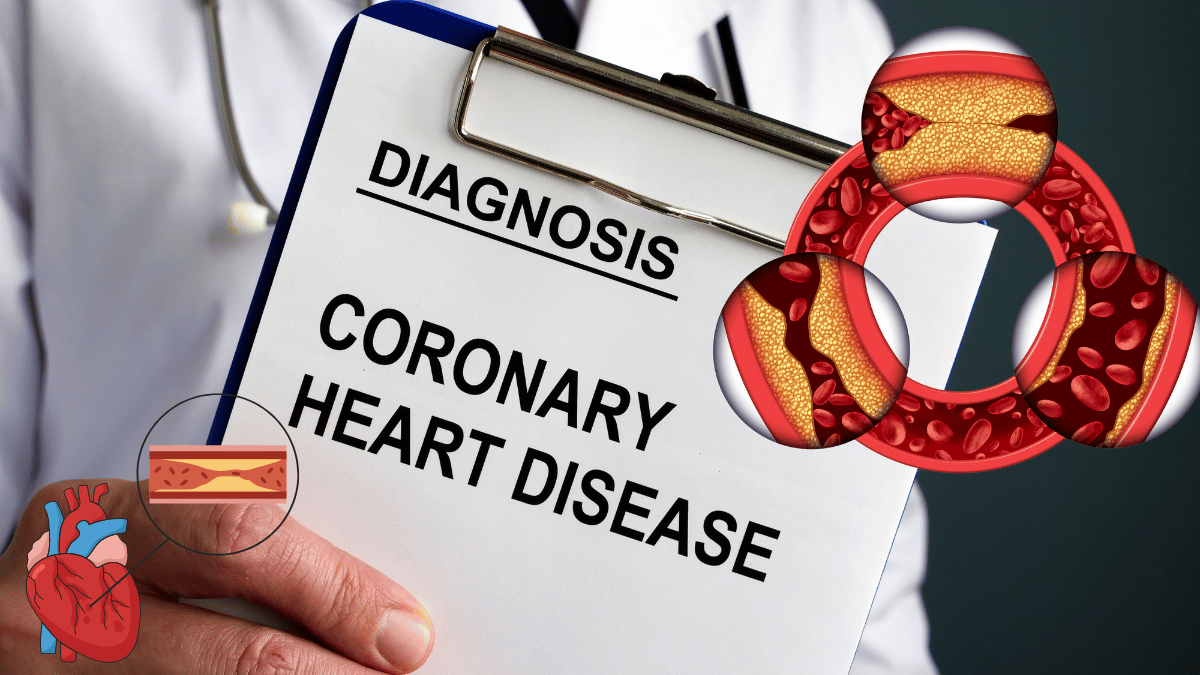
What is Coronary Artery Disease?
Symptoms of Coronary Artery Disease
Causes and Risk Factors
Major Risk Factors
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is influenced by several major risk factors that can increase an individual’s likelihood of developing the condition. Age is a significant factor, as the risk generally increases for men over 45 and women over 55. Genetics also play a critical role; a family history of heart disease can elevate the risk.
High blood pressure is another key contributor, as it can damage arteries over time, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup. High cholesterol levels, particularly elevated LDL (low-density lipoprotein), can lead to atherosclerosis, narrowing the arteries.
Additionally, diabetes significantly raises the risk, as high blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and accelerate plaque formation. Smoking is another major risk factor, as it harms the cardiovascular system and contributes to the development of CAD.
Lifestyle Choices that Contribute to CAD
Certain lifestyle choices can greatly influence the risk of developing coronary artery disease. Poor dietary habits, such as consuming high amounts of saturated fats, trans fats, and sugars, can lead to weight gain and contribute to high cholesterol and blood pressure levels.
Lack of physical activity is another critical factor; a sedentary lifestyle can result in obesity and reduced cardiovascular fitness, further increasing the risk of CAD. Stress is also a contributor; chronic stress can lead to unhealthy coping mechanisms like overeating or smoking, which can negatively impact heart health.
Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and lead to weight gain, compounding the risk factors for CAD.
Making healthier lifestyle choices, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, and avoiding tobacco and excessive alcohol, can significantly reduce the risk of developing coronary artery disease.
Treatment Options
Lifestyle Changes
Making lifestyle changes is often the first step in managing coronary artery disease (CAD) and can significantly impact overall heart health. A heart-healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help reduce cholesterol and blood pressure.
It’s important to limit the intake of saturated fats, trans fats, sodium, and added sugars. Regular physical activity is crucial; aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week can improve cardiovascular fitness and help maintain a healthy weight.
Additionally, stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga can contribute to better heart health. Quitting smoking and reducing alcohol consumption are vital changes that can lower the risk of complications associated with CAD. These lifestyle adjustments not only improve heart health but also enhance overall well-being.
Medications
Doctors often prescribe medications to help manage coronary artery disease and its symptoms.. Commonly used medications include statins, which help lower cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of heart attacks. Antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin, can prevent blood clots by reducing platelet aggregation.
Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors are often prescribed to help manage blood pressure and reduce strain on the heart. In some cases, medications to manage diabetes may also be necessary, as diabetes is a significant risk factor for CAD.
Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor the effectiveness of these medications and make adjustments as needed.
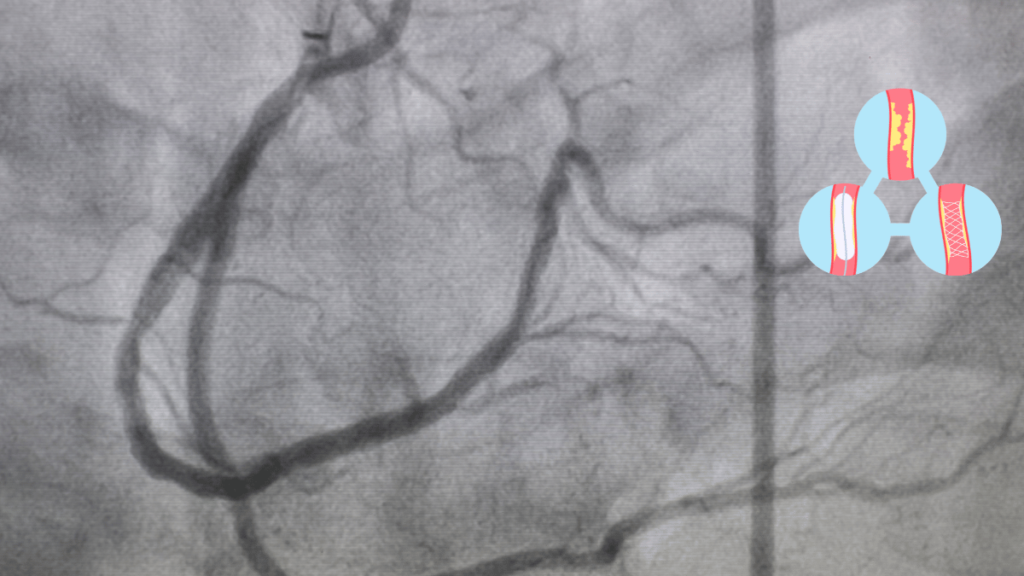
Surgical Interventions
In more severe cases of coronary artery disease, surgical interventions may be required to restore proper blood flow to the heart. One common procedure is angioplasty, where a small balloon is used to widen narrowed arteries, often followed by the placement of a stent to keep the artery open.
Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) is another option, where blood vessels from other parts of the body are used to create a bypass around blocked arteries, improving blood flow to the heart. These surgical procedures can significantly enhance quality of life and reduce the risk of heart attacks.
The choice of treatment depends on the severity of the disease, the patient’s overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions, highlighting the importance of personalized care in managing coronary artery disease.
Prevention Strategies
Healthy Eating Habits
Adopting healthy eating habits is a cornerstone of preventing coronary artery disease (CAD). A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps support heart health.
Incorporating sources of omega-3 fatty acids, such as fish, nuts, and seeds, can further reduce inflammation and lower cholesterol levels. It’s important to limit saturated fats, trans fats, and sodium, which can contribute to high blood pressure and cholesterol levels
. Additionally, being mindful of portion sizes can aid in maintaining a healthy weight. By making conscious food choices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing CAD and promote overall cardiovascular health.
Conclusion
Coronary artery disease is a significant health concern that affects millions worldwide, but understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to take control of their heart health.
Through lifestyle changes such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress, individuals can effectively reduce their risk of developing CAD. Medications and surgical interventions provide additional support for those with existing conditions.
Ultimately, a proactive approach that includes prevention strategies and regular medical check-ups can lead to a healthier life and a lower risk of serious cardiovascular events.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease is a condition characterized by the narrowing of coronary arteries due to plaque buildup.
What are the common symptoms of CAD?
Common symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and heart palpitations.
What causes coronary artery disease?
CAD is caused by factors like high cholesterol, high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.
How is coronary artery disease diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves medical history, physical exams, and tests such as ECGs, stress tests, and angiograms.
What lifestyle changes can help prevent CAD?
Healthy eating, regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding smoking are key prevention strategies.
What medications are used to treat CAD?
Common medications include statins, antiplatelet drugs, beta-blockers, and ACE inhibitors.